SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF CITRIC ACID-STABILIZED IRON OXIDE NANOPARTICLES FOR BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS
Main Article Content
Abstract
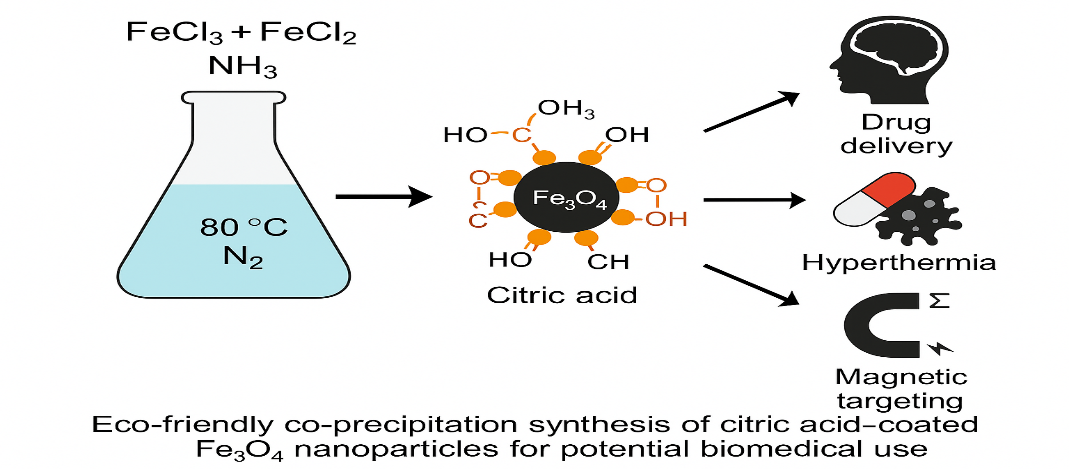
Iron oxide nanoparticles (MNPs) have emerged as a versatile class of nanomaterials with promising biomedical applications, particularly in targeted drug delivery, imaging, and diagnostics. This study reports the synthesis of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles via a chemical coprecipitation method, stabilized with citric acid to prevent aggregation and improve colloidal stability. The synthesized nanoparticles were thoroughly characterized using dynamic light scattering (DLS), zeta potential measurements, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results confirmed the successful synthesis of uniformly sized, spherical iron oxide nanoparticles with high crystallinity and surface stability. This foundational work sets the stage for the incorporation of these MNPs in advanced biomedical systems, including targeted drug delivery.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
[1] Lu, A. H., Salabas, E. L., & Schüth, F. (2007). Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization and application. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 46(8), 1222–1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602866
[2] Ianoș, R., Păcurariu, C., Muntean, S. G., Muntean, E., Nistor, M. A., & Nižňanský, D. (2018). Combustion synthesis of iron oxide/carbon nanocomposites, efficient adsorbents for anionic and cationic dyes removal from wastewaters. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 741, 1235–1246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.240
[3] Păcurariu, C., Paşka, O., Ianoş, R., & Muntean, S. G. (2016). Effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using a new magnetic iron oxide nanosorbent prepared by combustion synthesis. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 18(3), 705–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-015-1041-7
[4] Abu-Noqta, O., Aziz, A., & Usman, A. (2019). Colloidal stability of iron oxide nanoparticles coated
with different capping agents. Materials Today: Proceedings, 17, 1072–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.106
[5] Alzoubi, F. Y., Abu Noqta, O., Al Zoubi, T., Al-Khateeb, H. M., Alqadi, M. K., Abuelsamen, A., Makhadmeh, G. N. (2023). A novel one-pot synthesis of PVP-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as biocompatible contrast agents for enhanced T2-weighted MRI. Journal of Composites Science, 7(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7030131
[6] Al Zoubi, T., Albiss, B., Al-Akhras, M.-A., Qutaish, H., Alabed, E., & Nazrul, S. (2019). NiO nanofillers embedded in graphite/PVA-polymer matrix for efficient electromagnetic radiation shielding. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2083(1), 020002. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5094305
[7] Petcharoen, K., & Sirivat, A. (2012). Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Materials Science and Engineering B: Solid-State Materials for Advanced Technology, 177(5), 421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2012.01.003
[8] Benyoucef, M., Usman, M. A. U., Alzoubi, T., & Reithmaier, J. P. (2012). Pre-patterned silicon substrates for the growth of III–V nanostructures. Physica Status Solidi A, 209(8), 1579–1583. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201127513
[9] Al-Fandi, M., Oweis, R. J., Albiss, B. A., Alzoubi, T., Al-Akhras, M., Qutaish, H., Khwailah, H., Al-Hattami, S., Al-Shawwa, E. (2015). A prototype ultraviolet light sensor based on ZnO nanoparticles/graphene oxide nanocomposite using low temperature hydrothermal method. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 92, 012038. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/92/1/012038
[10] Osuna, Y., Gregorio-Jauregui, K. M., Gaona-Lozano, J. G., de la Garza-Rodríguez, I. M., Ilyna, A., Barriga-Castro, E. D., Saade, H., López, R. G. (2012). Chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles with low chitosan content prepared in one-step. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2012, 327562. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/327562
[11] Snoderly, H. T., Freshwater, K. A., Martinez de la Torre, C., Panchal, D. M., Vito, J. N., & Bennewitz, M. F. (2022). PEGylation of metal oxide nanoparticles modulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Biosensors, 12(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020123
[12] Cho, M., Villanova, J., Ines, D. M., Chen, J., Lee, S. S., Xiao, Z., Guo, X., Dunn, J. A., Stueber, D. D., Decuzzi, P., & Colvin, V. L. (2023). Sensitive T2 MRI contrast agents from the rational design of iron oxide nanoparticle surface coatings. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(2), 1057–1070. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c05390
[13] Wan, J., Jiang, X., Li, H., & Chen, K. (2012). Facile synthesis of zinc ferrite nanoparticles as non-lanthanide T1 MRI contrast agents. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 22(27), 13500–13505. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM30684K
[14] Benyoucef, M., Alzoubi, T., Reithmaier, J. P., Wu, M., & Trampert, A. (2014). Nanostructured hybrid material based on highly mismatched III–V nanocrystals fully embedded in silicon. Physica Status Solidi A, 211(1), 211–215. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201330214
[15] Braim, S. A., Shakesheff, K. M., Saunders, B. R., & Alexander, C. (2016). Biocompatible polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical use. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 4(5), 962–972. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB01958F
[16] Hammad, M., Hardt, S., Mues, B., Salamon, S., Landers, J., Slabu, I., Wende, H., Schulz, C., & Wiggers, H. (2020). Characterization of flame-made magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 824, 153814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153814
[17] Gumustas, M., Sengel-Turk, C. T., Gumustas, A., Ozkan, S. A., & Uslu, B. (2017). Multifunctional systems for combined delivery, biosensing and diagnostics. In A. M. Grumezescu (Ed.), Multifunctional Systems for Combined Delivery, Biosensing and Diagnostics (pp. 69–108). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-55725-5.00005-8
[18] Nayan, M. B., Jagadish, K., Abhilash, M. R., Namratha, K., & Srikantaswamy, S. (2019). Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles for water treatment applications. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 11(3), 357–370. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2019.113021
[19] Jones, J. A., Novo, N., Flagler, K., Pagnucco, C. D., Carew, S., Cheong, C., Kong, X. Z., Burke, N. A. D., & Stöver, H. D. H. (2005). Thermoresponsive polymers and their biomedical applications. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 43(24), 6095–6104. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.21041
[20] Frounchi, M., & Shamshiri, S. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of thermoresponsive magnetic hydrogels for drug delivery. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 103(6), 1893–1898. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.35336
[21] Yang, J., Zou, P., Yang, L., Cao, J., Sun, Y., Han, D., Yang, S., Wang, Z., Chen, G., Wang, B., & Kong, X. (2014). Surface modification of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Applied Surface Science, 303, 425–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.02.135
[22] Gubin, S. P. (2009). Magnetic nanoparticles: Introduction. In S. P. Gubin (Ed.), Magnetic Nanoparticles (pp. 1–9). Wiley-VCH. ISBN: 978-3-527-40790-2
[23] Omwoyo, W. N., Ogutu, B., Oloo, F., Swai, H., Kalombo, L., Melariri, P., Mahanga, G. M., & Gathirwa, J. W. (2014). Development and characterization of a liposomal nanocarrier for antimalarial drug delivery. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 9, 3865–3874. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S64018
[24] Obireddy, S. R., Chintha, M., Kashayi, C. R., Venkata, K. R. K. S., & Subbarao, S. M. C. (2020). Biopolymer-based magnetic nanocomposites for environmental and biomedical applications. ChemistrySelect, 5(33), 10276–10284. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202002605
[25] Park, J., Yu, M. K., Jeong, Y. Y., Kim, J. W., Lee, K., Phan, V. N., & Jon, S. (2009). Antibiofouling polymer-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for hepatoma-targeted imaging and therapy. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 19(41), 6412–6417. https://doi.org/10.1039/B904546A
[26] Yun, S. Y., Lee, J. Y., & Kim, J. (2020). Synthesis and characterization of Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 37(5), 875–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-020-0494-2
[27] Hammad, M., Hardt, S., Mues, B., Salamon, S., Landers, J., Slabu, I., Wende, H., Schulz, C., & Wiggers, H. (2020). Characterization of flame-made magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 824, 153814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153814